CDMO/CMO Mid-Year Review: Tracking the Key Moves Thus Far in 2023
As we near the mid-year mark, what have been the key moves—mergers and acquisitions, expansions, and new CDMOs entering the market—thus far in 2023? DCAT Value Chain Insights takes an inside look on what is on the industry’s radar.
Key developments thus far in 2023
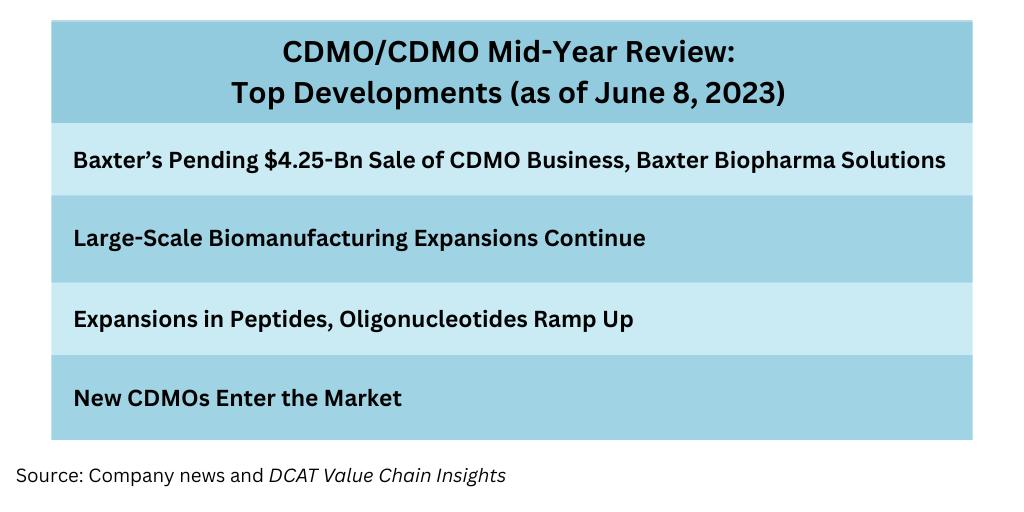
Baxter’s pending $4.25-billion sale of its CDMO business. Without question, the largest acquisition in the CDMO space thus far in 2023 is Baxter’s pending $4.25-billion sale of its CDMO business, Baxter BioPharma Solutions (BPS), to two private-equity firms: Advent International and Warburg Pincus. The deal was announced in May (May 2023) and is expected to close in the second half of 2023. The move is part of a larger plan by Baxter, which announced a series of actions in January (January 2023) to improve the company’s financial performance, which included evaluating strategic alternatives for its CDMO business.
BPS provides contract services for formulation development, sterile manufacturing, and lyophilization and parenteral delivery systems. The proposed transaction includes the CMDO’s manufacturing facilities in Bloomington, Indiana, and Halle, Germany. and approximately 1,700 employees. In announcing the sale of its CDMO business, Baxter said that BPS is expected to generate revenues of approximately $600 million on a reported basis for the full-year 2023.
Large-scale biomanufacturing expansions continue
Biomanufacturing continues to be an active area of investment for CDMOs/CMOs, with several CDMOs/CMOs proceeding or recently completing large-scale expansions as outlined below.
Samsung Biologics. This week (June 6, 2023), Samsung Biologics announced an updated timeline for its fifth biomanufacturing plant, which is to be constructed at a new second Bio Campus in Songdo, South Korea. The company is investing over KRW 1.9 trillion ($1.46 billion) in the new facility, which is scheduled to be operational in April 2025, and which will have production capacity of 180,000 liters. Samsung Biologics purchased 357,360 m2 of land in July 2022 for its Second Bio Campus, which will feature an Open Innovation Center for biotech incubation and four biomanufacturing plants with total capacity of 720,000 liters.
The company also recently completed the launch of its fourth manufacturing plant at its first Bio Campus in Songdo, South Korea, which encompasses four biomanufacturing plants with total capacity of 604,000 liters. Upon the completion of all plants at the company’s second Bio Campus, along with the future completion of the additional four biomanufacturing plants at its second Bio Campus, Samsung Biologics will hold a total biomanufacturing capacity of 1.324 million liters.
Lotte Biologics. Lotte Biologics is a new CDMO in the biologics space, having launched approximately one year ago and is proceeding with a KRW 3 trillion ($2.3-billion) expansion plan. Lotte Biologics entered the CDMO market with the acquisition of a commercial-scale biomanufacturing facility in Syracuse, New York, from Bristol-Myers Squibb in January (January 2023). Lotte Biologics is part of Lotte Corporation, a Seoul, Korea-based holding company with holdings in chemicals, food & beverage, retail, and hotels & services. The Syracuse facility will serve as the Lotte Center for North America Operations for Lotte’s biologics CDMO business in the US. Lotte acquired the Syracuse site’s operations and assets, which include the property, plant and equipment, and workforce.
In January (January 2023), the company announced a KRW 3 trillion ($2.3-billion) investment to build three biomanufacturing plants in Korea by 2030 to provide total production capacity of 360,000 liters. Each plant will be capable of producing 120,000 liters of antibody drugs, with additional expansion plans calling for a small-scale incubator for clinical drug-substance production as well as a commercial drug-product production facility. Construction of the first plant is slated to begin in the second half of 2023, with completion scheduled for the second half of 2025, GMP approval for the second half of 2026, and commercial production for 2027. Lotte says it aims to have all three plants fully operational by 2034. In addition, the new biomanufacturing site in Korea will host the Lotte Bio Campus, alongside a Bio-Venture Initiative, where biopharmaceutical start-ups can use Lotte’s facilities and establish a venue for cooperation.
Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies. Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies is investing $2-billion for a large-scale cell-culture biomanufacturing facility in Holly Springs, North Carolina. The company had announced the investment in January 2021. The facility is expected to be operational by the spring of 2025.
The company is also investing a combined $1.6 billion to expand manufacturing at its sites in Hillerød, Denmark, and College Station, Texas. The company is expanding to support large-scale cGMP fed-batch production by adding 8 x 20,000-L bioreactors and two downstream processing streams in its Hillerød, Denmark, facility to provide a total of 20 x 20,000-L bioreactors for drug-substance production as well as drug-product and finished goods services. Fujifilm Diosynth acquired the facility from Biogen in 2019 for approximately $890 million. The company is also adding a new cGMP production facility at its site in College Station, Texas, which will be operational by 2024, and which will double the company’s advanced therapy and vaccine manufacturing capacity in the US.
In April (April 2023), Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies announced that it had acquired 41 acres of land adjacent to its existing biomanufacturing campus in Research Triangle Park (RTP), North Carolina, to bring the total campus size to just under 119 acres to provide the company room to grow for future capacity for manufacturing and development of biologics. The company’s RTP campus is comprised of three main buildings, which include: over 170,000 square feet dedicated to GMP manufacturing of biologics; 151,000 square feet of process and analytical development laboratories, of which 89,000 square feet is part of a current expansion; and approximately 60,000 square feet of administration space. The company is currently expanding with the addition of a new BioProcess Innovation Center, which will double the site’s laboratory space and capacity to support process characterization programs. The expanded laboratories will be fully operational in the spring of 2024.
Lonza. Lonza is investing approximately CHF 850 million ($935 million) to add two mammalian drug-substance manufacturing facilities at its sites in Visp, Switzerland, and Portsmouth, New Hampshire. The expansion in Visp will add a new 27,500-square-meter large-scale mammalian drug-substance manufacturing facility. The facility is expected to be completed in 2024 with an investment of approximately CHF 650 million ($715 million). The expansion will complement the company’s existing large-scale biomanufacturing global network at its sites in Tuas, Singapore; Porriño, Spain; and Portsmouth, New Hampshire.
In Portsmouth, New Hampshire, the company is adding a new biomanufacturing facility for small-to-mid-volume production. The CHF 200-million ($220-million) facility will add capacity for up to eight 2,000-L single-use bioreactors to support Phase III clinical and commercial small- to mid-volume products. The facility is expected to be completed in 2023, and will complement the company’s existing single-use network at sites in Hayward, California; Slough, UK; Tuas, Singapore; and Visp, Switzerland.
WuXi Biologics. In November 2022, WuXi Biologics launched an integrated contract research, development and manufacturing (CRDMO) center in Fengxian, Shanghai, China. The 1.6-million-square-foot Integrated Biologics CRDMO Center is built with global cGMP standards and can accommodate more than 3,000 employees. The grand opening included research, development, one drug-substance manufacturing facility, and two drug-product facilities for clinical manufacturing at various scales and volumes. Once fully operational, it will be able to provide services from early discovery to commercial manufacturing, all within the center. Additionally, in China, the company released a 48,000-L commercial-scale GMP drug-substance manufacturing facility in Hebei, China, in October 2022.
Earlier this month (June 2023), the company announced that it is doubling the production capacity of its drug-substance biomanufacturing facility in Wuppertal, Germany, from 12,000 L to 24,000 L. Other recent developments include the company’s first manufacturing facility in the US in Cranbury, New Jersey. The site has 150,000 square feet of space with full development and clinical drug-substance and drug-product cGMP manufacturing capabilities. Drug-substance Phase I expansion was GMP-released in August 2022 with an initial capacity of 4,000 L, which upon completing Phase II, will grow to 6,000 L, using single-use technology. The drug-product facility will be ready for GMP formulation and fill-finish in 2024. In September 2022, the company announced that its 189,500-square-foot site in Worcester, Massachusetts, which is currently under construction, topped-off the steel of this commercial biomanufacturing facility. The company’s site in Dundalk, Ireland, was GMP-released in the fourth quarter of 2022, and received its first GMP Certificate from the Ireland Health Products Regulatory Authority. Overall, the company has a total estimated capacity of 580,000 L for drug-substance biopharmaceutical production planned by 2026 in the US, Ireland, Germany, Singapore, and China, and over 10 drug-product facilities supporting various presentations (liquid and lyophilization fills, vials, and prefilled syringes).
Expansions in Peptides, Oligonucleotides Ramp Up
A niche, but growing area of manufacturing expansion by CDMOs/CMOs is in peptides and oligonucleotides, with several companies announcing expansions.
Bachem. Bachem, a Bubendorf, Switzerland-headquartered CDMO of peptides and oligonucleotides, is proceeding with a billion-dollar plus investment plan to increase manufacturing capacity across its sites, including new facilities. The company is constructing a large-scale facility for the manufacture of peptides and oligonucleotides at its site in Bubendorf, Switzerland. The commissioning of the new large-scale peptide and oligonucleotide production plant in Bubendorf is planned for 2024 with the first phase operational in 2024 and a second phase operational in 2026. By 2030, a further production site is planned at a new site in Sisslerfeld in the municipality of Eiken, Canton of Aargau, Switzerland. In October 2022, Bachem announced its purchase of land for the new site in Sisslerfeld/Eiken. In all, Bachem is planning investments of CHF 550 million ($600 million) at its headquarters site in Bubendorf and CHF 750 million ($819 million) for the new site in Sisslerfeld/Eiken. Bachem is also investing in capacity expansions across its global manufacturing network at its sites in the following: Vionnaz, Switzerland; Torrance, California; Vista, California; and St. Helens, UK.
Agilent Technologies. In January (January 2023), Agilent Technologies, a Santa Clara, California-based technology company and CDMO of nucleic acid active pharmaceutical ingredients, announced it is investing approximately $725 million to double manufacturing capacity of therapeutic nucleic acids (i.e.,oligonucleotides) at its facility in Frederick, Colorado, by adding two new manufacturing lines. Agilent expects customer shipments from the expansion to begin in 2026.
WuXi STA. WuXi STA, a CDMO of drug substances and drug products, consolidated resources in a new brand, WuXi TIDES, to provide end-to-end contract research, development and manufacturing services for oligonucleotides, peptides, and their conjugates. In oligonucleotides, the company has six GMP solid-phase oligo synthesis (SPOS) production lines at its site in Changzhou, China. By 2024, the company will add more SPOS production lines. In April (April 2023), the company reported that it had added two 2,000-L reactors and a large-scale continuous purification system for peptide manufacturing at its Changzhou campus. With the two new 2,000 L reactors in operation, the total reactor volume of the solid-phase peptide synthesizers (SPPS) at WuXi TIDES increased to over 10,000 L. For peptides, the company plans to double its SPPS total reactor volume to more than 20,000 L in the future.
CordenPharma. CordenPharma, a CDMO of drug substances and drug products, announced this year (2023) that it is adding synthetic oligonucleotide manufacturing through a two-phase investment at its site in Colorado. Phase One involves reconditioning existing laboratory space, purchase of development equipment, and hiring of a team to set up process and analytical development capabilities. Target completion is expected in the fourth quarter of 2023. Phase Two, which is being initiated at the same time as Phase One, includes the redesign of existing manufacturing space to create a fully GMP-compliant manufacturing area housing synthesis, cleavage, downstream processing, and lyophilization at the 10–100 mmol scale for early- to mid-phase clinical trial material supply. The introduction of oligonucleotide manufacturing at its Colorado facility is an extension of its “Tides” capabilities, which includes peptide manufacturing. In CordenPharma Colorado, the company is investing approximately $30 million to build a new 1,000-L peptide synthesis line as part of an overall investment plan in peptide development and manufacturing.
New CDMOs Enter the Market
Reflecting the growth potential of biologics, including cell and gene therapies, several CDMOs recently entered the market in 2023.
An interesting move by a relatively new entity targeting the biologics CDMO market is from eureKING, a Paris-based special purpose acquisition company (SPAC) focused on bioproduction, which submitted an offer last month (May 2023) to acquire Skyepharma, a Saint-Quentin-Fallavier, France-based CDMO of oral drug technologies. eureKING was founded in March 2022 by eureKARE, an investment firm focused on financing and building companies in the fields of synthetic biology and the microbiome. eureKING’s plan is to invest in biologics CDMOs in three main areas: (1) the production of biologics, in particular new generations of monoclonal antibodies or complex proteins; (2) the production of cell and gene therapies; and (3) the production of live biotherapeutics (with applications in the microbiome). Skyepharma has what it calls its “Skyehub” model that hosts dedicated biomanufacturing facilities to allow customers to use the company’s quality system and, at the same time, preserve intellectual property. The Skyehub model has an initial focus on live biotherapeutic products. eureKING said that Skyepharma’s scalable and manufacturing platform would facilitate eureKING’s strategy to combine companies specializing in the production of biological products, cell and gene therapies, and live biotherapeutics.
Cell and gene therapies continues to be an area for new CDMOs, whether pure-play CDMOs or the contract manufacturing arm of bio/pharma companies developing cell and gene therapies. Some new CDMOs in this area launched thus far in 2023 include NewBiologix and Ascend Gene & Cell Therapies.
NewBiologix launched as a cell- and gene-therapy CDMO based in Lausanne, Switzerland. The company recently raised $50 million with funding led by Recipharm, a CDMO of small-molecule active pharmaceutical ingredients, biologics, and drug products, and the company’s co-founders, Igor Fish, the company’s CEO, and Nicolas Mermod, the company’s Senior Vice President, Research & Development. The company’s DNA-based platform is being developed to address manufacturing challenges associated with the production of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors. Specifically, the company’s technologies will be applied to human (HEK-293) and mammalian (CHO) cell lines. The company will begin beta testing the cell-line prototypes with key collaborators by 2024 and anticipates making viral production cell lines commercially available by 2026.
Ascend Gene & Cell Therapies. which was originally founded by Monograph Capital, an investment firm, launched this year after raising a total of $132.5 million. The company is focused on adeno-associated virus vectors. Its operations are headquartered in the UK with GMP production in Potters Bar, North London, platform technology research in the San Francisco Bay area, California, and a specialist process development and analytics team in Munich, Germany.