State of the State: AI in Procurement: Where Does It Stand?
The potential of AI to transform business functions, including procurement, is strong, but where does it actually stand? A recent analysis by the business and technology consulting firm, Gartner, provides a reality check for current and future adoption.
By Patricia Van Arnum, Editorial Director, DCAT, pvanarnum@dcat.org
Generative AI in sourcing and procurement.
How to apply artificial intelligence (AI) across business functions is top of mind, but where does AI stand in terms of adoption in sourcing and procurement functions? A recent analysis by the business and technology consulting firm, Gartner, examines the state of adoption of Generative AI in procurement, including the challenges to implement.
GenAI refers to AI techniques that learn a representation of artifacts from data and use it to generate brand-new, unique artifacts that resemble but do not repeat the original data. Generative AI can produce totally novel content (including text, images, video, audio, structures), computer code, synthetic data, workflows and models of physical objects.
GenAI for procurement has entered what Gartner calls the “trough of disillusionment.” While some early adopters are seeing benefits, many organizations are experiencing uneven return on investment or falling short of expectations, highlighting the need for a more measured and strategic approach, according to the analysis.
“GenAI is proving to deliver process efficiency, better data insights, and cost savings for procurement organizations,” said Kaitlynn Sommers, Senior Director Analyst in Gartner’s Supply Chain Practice, in a July 30, 2025, press release. “However, fragmented and low-quality data across procurement systems can hinder accurate outputs, and integrating stand-alone GenAI solutions with existing platforms is often complex due to differing technical specifications. Despite these challenges, its applicability across the source-to-pay spectrum continues to drive strong interest and adoption.”
To assess the current and future adoption of GenAI in sourcing and procurement functions, the firm uses the Gartner’s Hype Cycle for Procurement & Sourcing Solutions, a graphical depiction (see Figure 1) of a common pattern that arises with each new technology or other innovation through five phases of maturity and adoption.
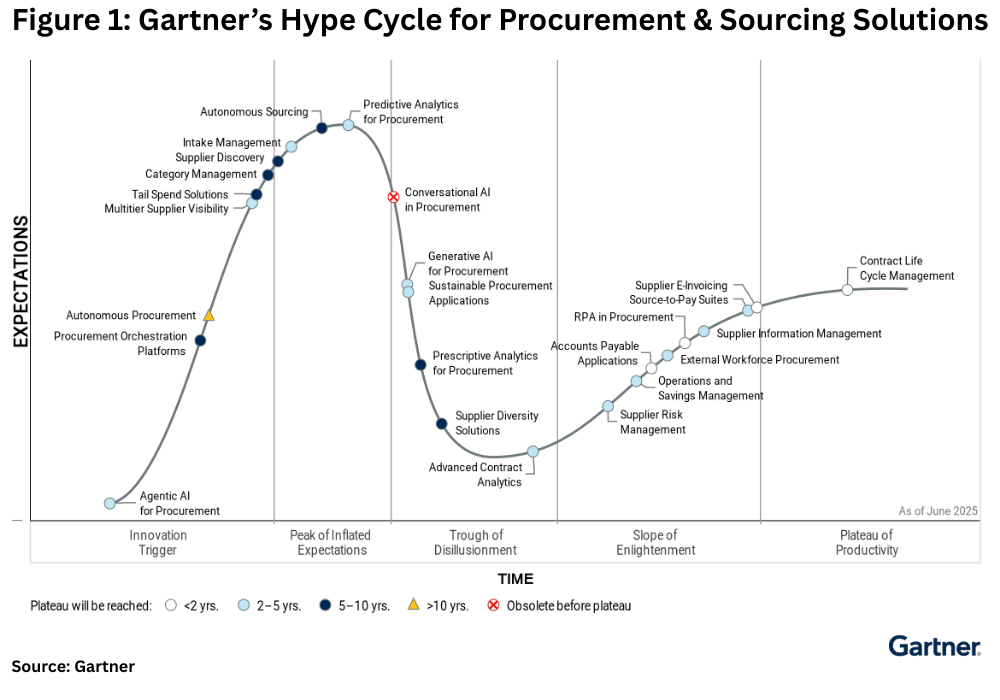
Each Hype Cycle drills down into the five key phases of a technology’s lifecycle. Figure 1 (see above) places specific procurement functions conducted through AI in these phases. These phases are outlined below.
Innovation Trigger: A potential technology breakthrough kicks things off. Early proof-of-concept stories and media interest trigger significant publicity. Often no usable products exist, and commercial viability is unproven.
Peak of Inflated Expectations: Early publicity produces a number of success stories — often accompanied by scores of failures. Some companies take action; many do not.
Trough of Disillusionment: Interest wanes as experiments and implementations fail to deliver. Producers of the technology shake out or fail. Investments continue only if the surviving providers improve their products to the satisfaction of early adopters.
Additional procurement technologies in the “trough of disillusionment,” where interest wanes after surpassing the peak of inflated expectations, include sustainable procurement applications, prescriptive analytics, supplier diversity solutions, and advanced contract analytics, with conversational AI in procurement now projected to become obsolete before reaching productivity
Slope of Enlightenment: More instances of how the technology can benefit the enterprise start to crystallize and become more widely understood. Second- and third-generation products appear from technology providers. More enterprises fund pilots; conservative companies remain cautious.
Plateau of Productivity: Mainstream adoption starts to take off. Criteria for assessing provider viability are more clearly defined. The technology’s broad market applicability and relevance are clearly paying off.
GenAI for procurement: applications
GenAI-enabled procurement applications will focus on automating time-consuming, repetitive tasks such as knowledge discovery, summarization, contextualization, workflow, and execution, according to the Gartner analysis. As these tools are adopted, procurement organizations can expect to boost productivity and efficiency, reduce operational costs, and free up staff to focus on higher-value activities such as strategic decision-making and supplier management.
Common use cases for GenAI in procurement
Text-to-process and workflow automation are emerging as common use cases for GenAI in procurement by enabling users to generate workflows or instruct agents using natural language, according to the Gartner analysis. These capabilities support tasks such as automating contract management, project scoping, supplier recommendations, and autogenerating “Request For” documents (RFx). GenAI offers the potential for significant cost savings while maintaining or even improving output quality, and early adopters are positioned to gain a strategic edge over competitors.
GenAI for procurement: adoption obstacles
Organizations face several obstacles in adopting GenAI for procurement, including fragmented and low-quality data, job security concerns, skepticism about AI-driven insights, and resistance to change, according to the Gartner analysis. High and unpredictable costs, complex integration with existing systems, and emerging regulatory requirements further complicate adoption. Unclear regulations also raise concerns around privacy, intellectual property protection, and trust.
“Organizations that delay action on integrating GenAI into procurement processes risk falling behind as early adopters overcome these challenges and realize tangible benefits,” said Sommers. “Gartner projects that GenAI for procurement will become a fully productive technology within five years.”
For chief procurement officers seeking to integrate GenAI into their operations, Gartner provides some key points in its adoption as outlined below.
- Data infrastructure. Invest in data infrastructure to standardize and integrate information across procurement systems for more reliable insights.
- Embedded GenAI capabilities. Explore vendors offering embedded GenAI capabilities and assess how these solutions align with enterprise strategies and desired business outcomes.
- Process-specific AI tools. Evaluate process-specific AI tools for areas such as sourcing, contract management, and supplier risk where early adopters are seeing benefits.
- Change management. Prioritize change management by encouraging learning and adaptation of procurement processes using data insights and automation.
- Regulatory considerations. Monitor evolving regulations to ensure compliant implementation and seek expert guidance as needed.
- Upskill talent. Upskill teams in digital dexterity, human-machine interaction, and prompt engineering to prepare for more AI-enabled processes.
Other AI technologies: beyond GenAI
In a separate analysis, Gartner provided insights into the overall adaption of AI technologies, pointing to AI agents and AI-ready data as the two fastest advancing technologies on the 2025 Gartner Hype Cycle for Artificial Intelligence (see Figure 2). Gartner Hype Cycles provide a graphic representation of the maturity and adoption of technologies and applications, and how they are potentially relevant to solving real business problems and exploiting new opportunities. The Gartner Hype Cycle methodology gives a view of how a technology or application will evolve over time to provide a sound source of insight to manage its deployment within the context of specific business goals.
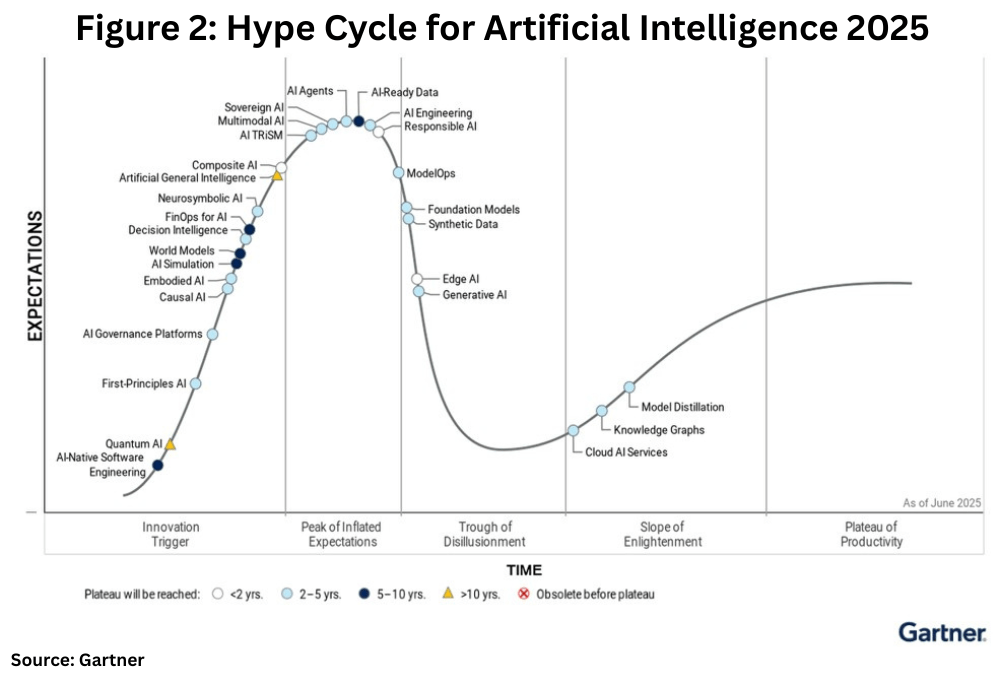
“With AI investment remaining strong this year, a sharper emphasis is being placed on using AI for operational scalability and real-time intelligence,” said Haritha Khandabattu, Senior Director Analyst at Gartner,” in an August 4, 2025, press release. “This has led to a gradual pivot from generative AI (GenAI) as a central focus, toward the foundational enablers that support sustainable AI delivery, such as AI-ready data and AI agents.”
Among the AI innovations Gartner expects will reach mainstream adoption within the next five years are multimodal AI and AI trust, risk and security management (TRiSM), which have been identified as dominating the Peak of Inflated Expectations. Together, these developments will enable more robust, innovative and responsible AI applications, transforming how businesses and organizations operate. Outlined below are some key AI technologies outlined in the Gartner analysis and their potential and challenges to implementation.
AI agents. AI agents are autonomous or semiautonomous software entities that use AI techniques to perceive, make decisions, take actions, and achieve goals in their digital or physical environments. Using AI practices and techniques, such as large language models (LLMs), organizations are creating and deploying AI agents to achieve complex tasks. LLMs are AI systems capable of understanding and generating human language by processing vast amounts of text data.
“To reap the benefits of AI agents, organizations need to determine the most relevant business contexts and use cases, which is challenging given no AI agent is the same and every situation is different,” said Gartner’s Khandabattu. “Although AI agents will continue to become more powerful, they can’t be used in every case, so use will largely depend on the requirements of the situation at hand.”
AI-ready data. AI-ready data ensure datasets are optimized for AI applications to enhance accuracy and efficiency. Readiness is determined through the data’s ability to prove its fitness for use for specific AI use cases. It can only be determined contextually to the AI use case and the AI technique used, which forces new approaches to data management, according to the Gartner analysis.
According to Gartner, organizations that invest in AI at scale need to evolve their data-management practices and capabilities to extend them to AI. This will cater to existing and upcoming business demands, ensure trust, avoid risk and compliance issues, preserve intellectual property, and reduce bias and hallucinations (which refers to situations where LLMs generate outputs that are false, misleading or factually incorrect).
Multimodal AI. Multimodal AI models are trained with multiple types of data simultaneously, such as images, video, audio, and text. By integrating and analyzing diverse data sources, they can better understand complex situations better than models that use only one type of data, according to the Gartner analysis. Multimodal AI will become increasingly integral to capability advancement in every application and software product across all industries over the next five years, according to Gartner research.
AI TriSM. AI TRiSM plays an important role in ensuring ethical and secure AI deployment. It comprises four layers of technical capabilities that support enterprise policies for all AI use cases and help assure AI governance, trustworthiness, fairness, safety, reliability, security, privacy, and data protection.
“AI brings new trust, risk and security management challenges that conventional controls don’t address,” said Khandabattu. “Organizations must evaluate and implement layered AI TRiSM technology to continuously support and enforce policies across all AI entities in use.”