The Innovation Leaders: A View from the C-Suite
In a special program at DCAT Week, Aamir Malik, Executive Vice President and Chief Business Innovation Officer, Pfizer, provides industry reflections on the drivers and key trends in new drug development.
Product innovation: key trends
New product development is the lifeblood of the Bio/Pharmaceutical industry, so what are some key trends in product innovation?
Consider some key facts. In 2021, the US Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) approved 50 new molecular entities (NMEs), referring to new active substances, which was on par with the number of NMEs approved in 2020 and which continued a strong trajectory for new drug approvals. In 2020, FDA’s CDER approved 53 NMEs, which was the second-highest level of NMEs approved in a given year in the past decade, except for 2018 when 59 NMEs were approved (see Figure 1).
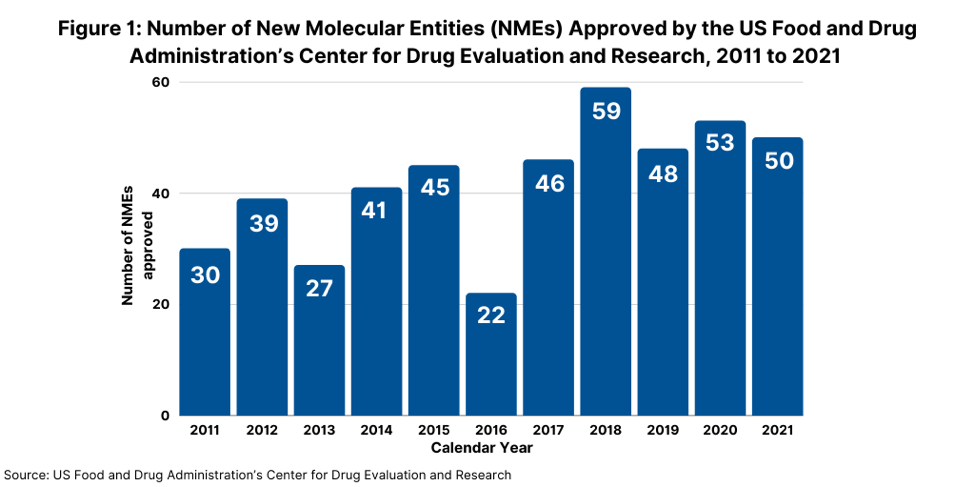
Of the 50 NMEs approved in 2021, more than half (54%) were characterized by the FDA’s CDER as being “first in class,” meaning drugs having mechanisms of action different from those of existing therapies. This level of first-in-class NME approvals represented a recent high. In 2020, 40%, or 21, of the 53 NMEs approved were characterized as “first-in-class” and in 2019, 42%, or 20, of the 48 novel drugs approved, were defined as “first-in-class.”
Another important trend in new drug approvals is product mix: small molecules versus biologics. Small-molecule drugs dominated NME approvals in 2021. Of the 50 NMEs approved in 2021, 36, or 72%, were small molecules, and 14, or 28%, were biologics. This continues a recent trend of having approximately three-fourths of NME approvals be small molecules. In 2020, 75%, or 40, of the 53 NMEs were small molecules. In 2019, 79% of NME approvals were small molecules; in 2018, it was 71% and 74% in 2017. Separate from this mix is the rise of new modalities, such as cell and gene therapies, which are approved by the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research.
Another key trend is the increasing share of orphan drugs in new drug approvals. In 2021, 26 of CDER’s 50 new drug approvals (52%) were approved to treat rare or “orphan” diseases (i.e., diseases that affect less than 200,000 people in the US). This continues a recent trend in which approximately 40% to roughly 50% of NME approvals were for orphan drugs. In 2020, 58%, or 31, of the 53 NME approvals in 2020 were for orphan drugs. The 58% of NME approvals in 2020 matched a recent high in the share of orphan drugs in NME approvals; in 2018, 58%, or 34, of the 59 NMEs approved were orphan drugs.
Industry perspectives: a C-suite view
More than just the numbers, however, is what is behind product innovation and what will drive new drug development in the future. Adapting new models in R&D, including approaches in external innovation/partnering and the role of digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence, are important factors in determining future R&D productivity. Equally important is the decision criteria used in portfolio optimization, both for pipelines and commercial products. These choices for where R&D dollars go and the factors influencing time to market and commercial success are crucial.


Executive Vice President & Chief Business Innovation Officer
Pfizer
To gain a perspective on these issues, Aamir Malik, Executive Vice President and Chief Business Innovation Officer, Pfizer, will sit down in a one-on-one interview at DCAT Week 2022, in The Innovation Leaders program on Tuesday, March 22, from 2:30 to 3:30 PM. He will provide his views on the key issues shaping current and future drug development and the factors impacting product innovation in the Bio/Pharmaceutical industry. In his role at Pfizer, Mr. Malik is responsible for the company’s strategy, business development, portfolio management, pipeline prioritization, and formation of new business ventures, as well as the advancement of innovative access partnerships with payers and governments around the world.
The program will provide valuable insights to both Bio/Pharma companies and their suppliers to better understand how their companies can stay at the forefront of product innovation. Further information, including how to register, may be found here.








